The Value of Specialist Concrete Scanning Services
The Value of Specialist Concrete Scanning Services
Blog Article
Past the Surface: Leveraging Advanced Concrete Scanning Techniques for Unmatched Precision and Understanding
In the world of construction and facilities upkeep, the quest for accuracy and thoroughness is never-ending. Advanced concrete scanning strategies have actually emerged as vital tools in this quest, supplying a glimpse under the surface to unveil a globe of essential understandings. By taking advantage of advanced modern technologies, specialists can discover anomalies, examine the problem of concrete structures, and make educated choices that form the course of tasks. The ramifications of these techniques expand much past mere surface-level examinations, promising a depth of accuracy and understanding that is unequaled.
Significance of Advanced Concrete Scanning
The relevance of using advanced concrete scanning strategies depends on the unparalleled accuracy they use for spotting sub-surface abnormalities and making sure architectural integrity. By using sophisticated modern technologies such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR), electro-magnetic induction, and progressed finder imaging, construction professionals can dig underneath the surface of concrete frameworks with a level of accuracy that much exceeds traditional assessment approaches. Concrete Scanning. These strategies allow the identification of covert threats like rebar rust, voids, conduits, or post-tension wires that might jeopardize the stability and safety of a structure gradually
In addition, advanced concrete scanning gives important understandings into the general problem of a concrete component without the demand for invasive actions, reducing the risk of triggering damages during the assessment process. The ability to identify the precise place and depth of possible problems enables targeted fixings and upkeep, inevitably lengthening the lifespan of the framework and optimizing its performance. Essentially, the importance of advanced concrete scanning can not be overstated in the realm of construction and framework maintenance, where precision and dependability are vital.
Kinds of Cutting-Edge Technologies

Abnormalities and Problem Discovery
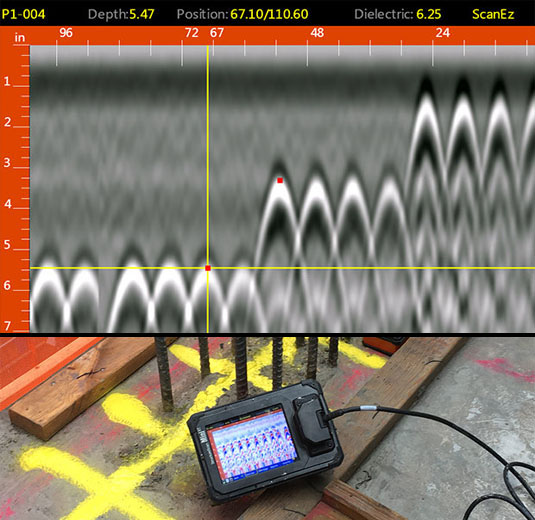
In enhancement to GPR, concrete scanning strategies like thermography and impact-echo testing are additionally reliable in finding defects and abnormalities. By leveraging these innovative strategies, specialists can proactively deal with architectural problems, ensuring the durability and safety of concrete structures.
Assessing Concrete Problem
Just how can designers accurately examine the problem of concrete frameworks to ensure their long life and safety and security? Numerous innovative concrete scanning methods are used for this objective. Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is typically used to examine the inner framework of concrete, detecting gaps, fractures, and other anomalies that might compromise its toughness.
Furthermore, aesthetic inspection continues to be an essential part of concrete problem evaluation. Engineers aesthetically analyze the surface area for indicators of degeneration, such as spalling, cracking, or staining. Integrating non-destructive testing techniques with aesthetic inspections sites permits for a comprehensive evaluation of concrete condition, making it possible for designers to identify potential concerns beforehand and execute prompt upkeep or repairs. By leveraging these advanced strategies, engineers can make sure the long-term toughness and safety of concrete structures.
Enhancing Decision-Making Procedures
In the realm of framework management, optimizing decision-making processes is vital for guaranteeing the reliable maintenance and long life of concrete structures. Boosted decision-making procedures in concrete administration involve using innovative scanning techniques to collect comprehensive data on the condition of frameworks. By leveraging modern technologies such as ground-penetrating radar and 3D imaging, stakeholders can make informed choices regarding fixing, reinforcement, or substitute strategies.
These progressed scanning techniques give important insights right into the inner make-up of concrete, determining possible problems such as voids, fractures, or rust that might not be visible externally. This level of comprehensive info permits aggressive upkeep planning, lessening the risk of structural failures and raising the total life expectancy of concrete frameworks.
Additionally, by including electronic documents and evaluation devices right into the decision-making procedure, stakeholders can track the advancement of concrete problems over time, allowing predictive upkeep techniques and maximizing source allotment. Ultimately, the combination of innovative concrete scanning methods improves decision-making processes by supplying unmatched accuracy, insight, and performance in facilities management.
Final Thought
In verdict, progressed concrete scanning strategies offer unparalleled accuracy and understanding in identifying anomalies, issues, and assessing the problem of concrete structures. By leveraging innovative modern technologies, decision-making processes can be enhanced, bring about even more informed and efficient services for keeping and fixing concrete infrastructure. These techniques play a vital duty in making certain the security and longevity of concrete frameworks, making them an essential device in the area of construction and design.
Furthermore, advanced concrete scanning go to these guys provides important understandings into the total condition of a concrete element without the demand for intrusive procedures, lessening the danger of triggering damage during the analysis procedure - Concrete Scanning. Another ingenious technology is 3D X-ray scanning, which provides thorough photos of the inner framework of concrete, providing valuable information without description the demand for damaging testing. Additionally, Concrete Cover Meters are used to gauge the density of concrete cover over reinforcement bars properly. Enhanced decision-making procedures in concrete management include using innovative scanning strategies to gather comprehensive information on the condition of structures.In conclusion, progressed concrete scanning strategies use unmatched accuracy and insight in spotting anomalies, flaws, and evaluating the condition of concrete frameworks
Report this page